Establishment of sustainable and independent farm household economy in the rural areas of Indochina
Related Research Program
Rural Livelihood Improvement
2021-03-02
東南アジア諸国連合(ASEAN)の諸国はこれまで順調に経済発展してきましたが、一方では加盟国間の経済格差が拡大し、域内の後発途上国への経済支援による底上げが急務となっています。そのため農林水産業においても商業的展開を通じた所得・生計向上方策が求められています。
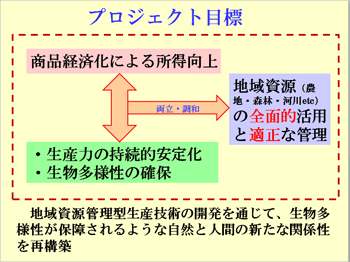
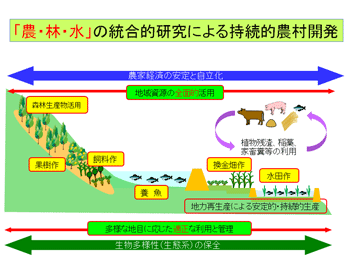
本プロジェクトでは、ラオス農山村を主な対象地域として、多種多様な地域資源を全面的に活用すること、適正な管理の実践論理を発展的に継承させた生産諸技術を開発すること、それらを総合的に現地実証することによって、持続的で安定的かつ自立的な営農が保障されるような商品経済化の具体的方向を提案します。このことは生態系保全や生物多様性が保障されるような新たな自然と人間の関係性を、地域資源管理型生産諸技術の開発を通じて現代的に再構築することでもあり、後発途上国にとどまらず資源収奪・生態系破壊型展開の弊害を抱える先進諸国にとっても有益な示唆となります。
このような理念と目的に沿って、次の研究課題と項目を設定しています。
- ラオス農山村における自給生産の持続的安定性の向上
小規模・簡易型灌漑、低投入型稲作栽培、持続的漁撈手法、持続的森林活用 - ラオス農山村における商品生産の拡大と持続性確保
水田高度利用、持続的畑作生産、安定的飼料基盤、安定的果樹生産 - ラオス農山村における農家経済の安定化及び自立度向上のための社会経済的条件
水田作・畑作関連技術の評価、複合経営の成立条件 - ラオス農山村における生物多様性の評価と保全
生物多様性の指標化とそれを活用した農村開発手法の開発