Pick Up
915. QTL Allele from Wild Soybean Enhances Protein Content without Reducing Oil Content
915. QTL Allele from Wild Soybean Enhances Protein Content without Reducing Oil Content
Soybean seeds contain approximately 40% protein and 20% oil. Also, soybean is the most important protein and oil source for human consumption. Over 71% of the world's vegetable protein and 29% of the world's oil comes from soybeans. However, soybean protein content is negatively correlated with oil content, making it difficult to develop varieties with high levels of both. Wild soybean, the ancestor of soybean, has a higher protein content in seeds than cultivated soybean. Therefore, wild soybean has attracted attention as an important genetic resource for improving the protein content of cultivated soybean varieties.
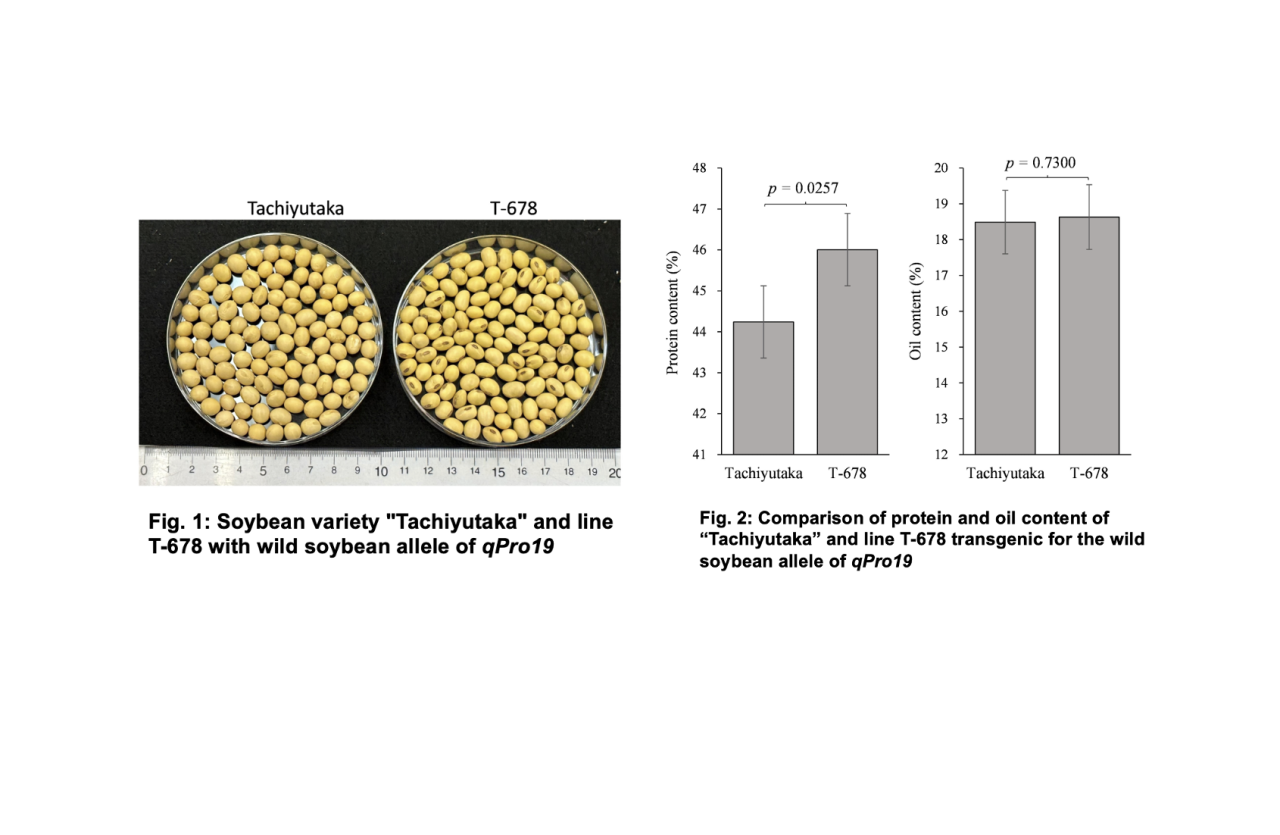
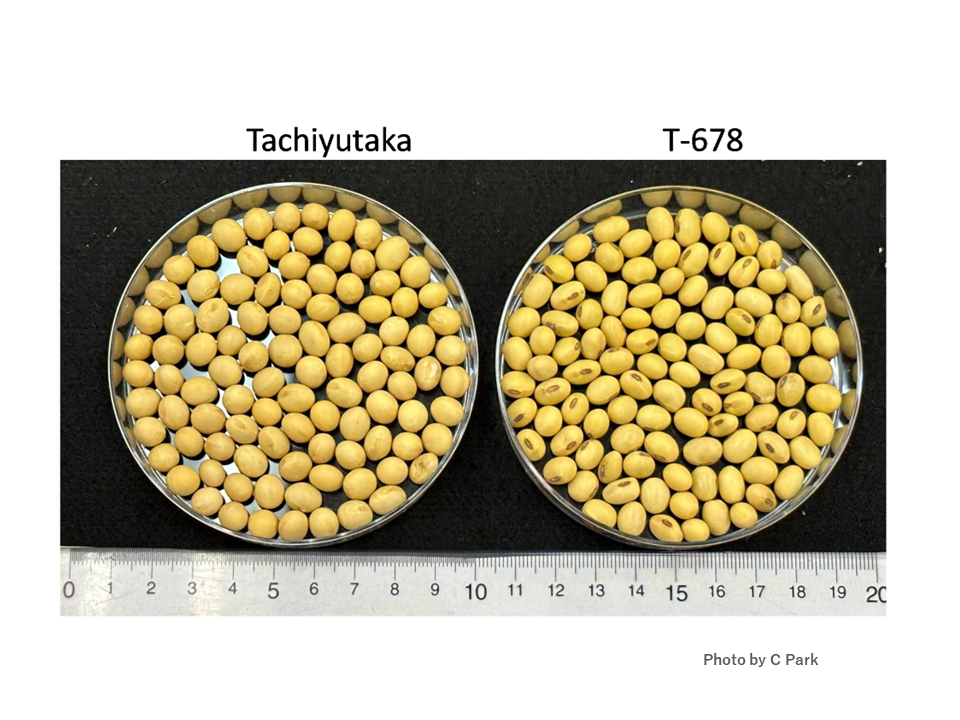
To identify genes from wild soybean that increase protein content, JIRCAS created a chromosome segment substitution line (CSSL) population by crossing a soybean variety with a wild soybean accession (JIRCAS Research Highlight 2018, Development of wild soybean chromosome segment substitution lines for genetic studies of important traits). In the present study, a total of 113 wild soybean CSSLs were cultivated in the field for three years (2018, 2019, and 2020). These lines were also evaluated for seed protein and oil content. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis was performed using 243 SSR markers. As a result, 12 QTLs associated with seed protein, oil and protein + oil content were identified on 8 chromosomes. Among them, the wild soybean allele of the QTL (qPro19) located on chromosome 19 did not reduce seed oil content, but only increased protein content. In addition, by introducing the identified wild soybean allele of qPro19 into a soybean cultivar "Tachiyutaka", we obtained a BC4 line T-678 that had increased protein content without reducing oil content (Figures 1 and 2). This study suggests that alleles from wild soybean could be potential genetic resources for breeding programs aimed at improving soybean seed quality.
References
Park, C., Nguyen, T. T., Liu, D., Xu, D. (2023) A QTL allele from wild soybean enhances protein content without reducing oil content. Plant Genetic Resources- Characterization and Utilization. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1479262123000850
Development of wild soybean chromosome segment substitution lines for genetic studies of important traits https://www.jircas.go.jp/en/publication/research_results/2018_b04
Contributor: PARK Cheolwoo (Biological Resources and Post-harvest Division)