Rice innovation for environmentally sustainable production systems
2025-08-04
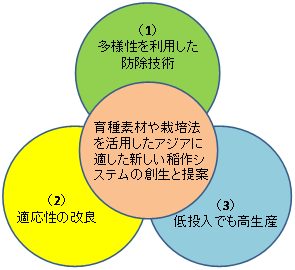
In Asian rice cultivation, a lot of chemicals for fertilizers and pesticides have been utilized thus higher yields were achieved in developed and developing countries. On the other hand, too much application of chemicals induced environmental pollution. And the increased prices of chemicals recently created serious problems especially in developing countries. A low input and environment-friendly strain of rice and new cultivation technology that ensures stable productivity in poor environmental conditions will be advanced in Asia.
Development of breeding lines, such as multiline varieties, for practical usage through the Blast Research Network for stable rice production that was prior established, will be undertaken. Regarding tolerance to phosphate deficiency, zinc deficiency, iron toxicity and ozone, the project shall pursue elucidation of the genetic factors and evaluation of breeding materials. Furthermore, stable and highly productive rice strains and new cultivation methods/system will also be developed through genetic and physiological improvements of nitrogen use efficiency in rice plants.
The project will likewise establish a system of high-yielding technologies under low input conditions. Contribution to the promotion of the project, "Development of rice production technologies in Africa", as mentioned previously, shall be through the research on “Improvement of Asian-style rice cultivation.”
(1) 国際的なネットワークと多様性を生かしたいもち病防除技術の開発
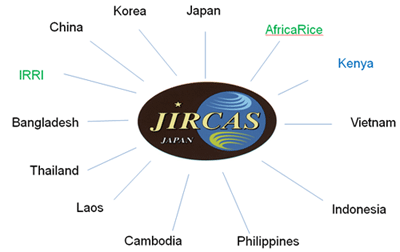
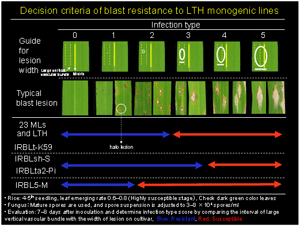
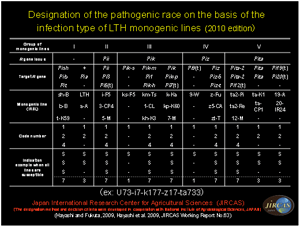
日本を含めた9か国の17の研究機関および大学、さらに国際研究機関としての国際稲研究所やアフリカ稲センターと連携を行い、国際的なネットワーク研究を展開しています。 このネットワーク研究では、いもち病菌レースやイネの抵抗性遺伝子を同定できる判別システムの構築と、いもち病菌レースやイネ遺伝資源の世界的な分布や多様性を解明します。このため、共通した判別品種の開発・普及、抵抗性評価基準の提案・普及を進めており、国際稲研究所とは判別品種群の開発、(独)農業生物資源研究所とはいもち病菌の病原性判定基準やレース命名法を作成しました。病原性判定基準については、12か国の言語[日本、英国、韓国、中国、インドネシア、フィリピン、タイ、ベトナム、ラオス、スペイン、ポルトガル、フランス]に翻訳し配布しています。これら判別システムと、いもち病菌レースや抵抗性遺伝資源の情報をもとに、各国での新規抵抗性遺伝子の探索・同定、イネ品種の抵抗性の改良を行います。 具体的には、農薬をできるだけ少なくするため、様々ないもち病抵抗性遺伝子の遺伝子型を持った同質遺伝子系統群としての多系品種の開発や多くのいもち病菌系に対して効果のある圃場抵抗性遺伝子の利用など、生物学的多様性を生かした防除技術の開発を目指します。 ネットワーク研究で見つけられた情報、あるいは開発された材料(判別品種群、新規抵抗性遺伝子、多系品種)は、参画研究機関間で交換し、相互の研究を補完しあうようなことも目指します。
JIRCASの展開する国際的いもち病研究ネットワーク(2011年現在)
|
|
(2) 適応性を改良した環境ストレス耐性イネの開発
熱帯地域での問題土壌では、リン酸欠乏、亜鉛欠乏、鉄毒などが重要な育種課題として残されています。また環境汚染等により生じるオゾンについても、これまでの先進国とともに発展途上国の工業化に伴いその被害が拡大してくると考えられます。 これら環境ストレスに対する耐性遺伝子の探索・同定、さらには効率的に育種を進めていくための分子生物学的解析により開発された選抜(DNA)マーカーの開発を進めていきます。また同時に、有用な育種素材の開発も進めます。
(3) 低投入でも高い生産性を確保できるイネ品種の開発
イネ品種そのものの窒素利用効率を向上させ、少ない肥料でも乾物生産や収量を確保できる新しいイネを開発します。このため、イネの草型[穂型]、根型などの改良とともに、窒素反応や利用に関する遺伝子の探索や育種素材開発を進めます。 またイネの品種改良とともに、それら育種素材が最も適応した栽培方法も検討します。