Identification of QTL for efficient root elongation under a wide range of nitrogen concentrations in a rice variety with an Indica-type genetic background
Description
Because root is the sole organ for uptaking water and nutrients such as nitrogen from surrounding soils, improving root architecture and physiological functions are required for enhancing stability and production in rice. IR64, an elite Indica-type variety with high adaptability and high yield, has been widely accepted as a mega variety in rice production and breeding programs in many tropical regions. The International Rice Research Institute—Japan Collaborative Research Project has developed a total of 334 introgression lines (ILs) derived from ten high yielding donor varieties with the genetic background of IR64. Among them, a line designated as YTH183 showed stable and higher yield in tropical regions as well as in temperate regions compared with IR64. However, quantitative trait locus/loci (QTL) for the stable and higher yielding line have not been identified. Furthermore, QTL for root elongation efficiently under a wide range of nitrogen concentrations have not been identified in varieties with the genetic background of IR64. The aims of this study, therefore, were to map and characterize the QTL derived from YTH183 to understand the architecture and functions of roots in YTH183.
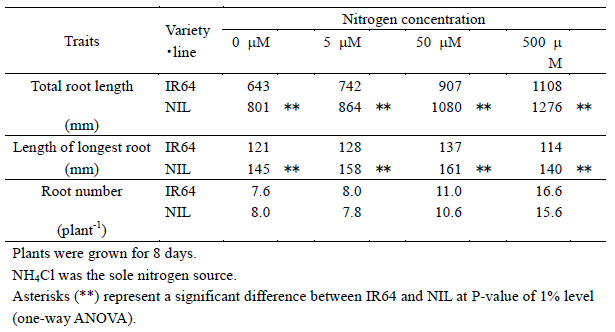
The longest root of YTH183 was significantly higher than that of IR64 seedlings hydroponically grown for 8 days in 5 μM NH4Cl (Fig. 1). As a result, YTH183 had a QTL for root elongation, designated as qRL6.4-YP5. The longest root of near-isogenic line (NIL) for qRL6.4-YP5 with the genetic background of IR64 was significantly higher than that of IR64 (Fig. 1). The QTL qRL6.4-YP5 (R2=0.37) was identified in the flanked region between RM6395 and RM8242 on the long-arm region of chromosome 6 (Fig. 2). Further characterization of qRL6.4-YP5 was done using the NIL. Compared with IR64, total root length was always higher in the NIL and was enhanced in response to the increase in exogenous concentrations of nitrogen (Table 1). The length of the longest root was always higher in the NIL. It was enhanced under nitrogen concentrations of up to 50 μM NH4Cl, but not in 500 μM NH4Cl (Table 1). The effect of qRL6.4-YP5 on root number was not proven in these conditions (Table 1).
To our knowledge, qRL6.4-YP5 is the first promising QTL for efficient root elongation under a wide range of nitrogen concentrations in rice varieties with the genetic background of IR64. These achievements should help improve root architecture of rice for a stable and high yielding production system in tropical developing countries.
Figure, table
-
Fig. 1. Typical phenotypes of seedlings grown for 8 days in 5 μM NH4Cl. YTH183 and NIL have positive allele of qRL6.4-YP5. Scale bar in individual pictures indicates 50 mm.
-
Fig. 2. Physical position of qRL6.4-YP5 on the long-arm region of chromosome 6. Closed vertical column indicates candidate region for qRL6.4-YP5. Closed triangle indicates the position of the peak F score.
-
Table 1. Elongation and development of roots in NIL for qRL6.4-YP5 under a wide range of nitrogen concentrations
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Biological Resources and Post-harvest Division
- Classification
-
Administration A
- Research project
- Program name
- Term of research
-
FY 2014 (FY 2011-FY 2015)
- Responsible researcher
-
Obara Mitsuhiro ( Biological Resources and Post-harvest Division )
Ishimaru Tsutomu ( Biological Resources and Post-harvest Division )
Abiko Tomomi ( Kyushu University )
Fujita Daisuke ( Institute of Crop Science, NARO )
KAKEN Researcher No.: 80721274Kobayashi Nobuya ( Institute of Crop Science, NARO )
KAKEN Researcher No.: 70252799Yanagihara Seiji ( Biological Resources and Post-harvest Division )
MIERUKA ID: 001780Fukuta Yoshimichi ( Tropical Agriculture Research Front )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-014-0320-9
Obara et al. (2014) Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 8:267-277.
- Japanese PDF
-
2014_B07_A3_ja.pdf174.56 KB
2014_B07_A4_ja.pdf298.94 KB
- English PDF
-
2014_B07_A3_en.pdf80.14 KB
2014_B07_A4_en.pdf160.04 KB
- Poster PDF
-
2014_B07_poster.pdf277.93 KB