研究成果
Elucidating the Leaf Vein Structure and Function of Tropical Rainforest Trees
― Understanding Leaf Vein Structure Contributes to the Selection of Trees with High Adaptability to the Environment―
Elucidating the Leaf Vein Structure and Function of Tropical Rainforest Trees
―Understanding Leaf Vein Structure Contributes to the Selection of Trees with High Adaptability to the Environment ―
|
Main Points
|
Overview
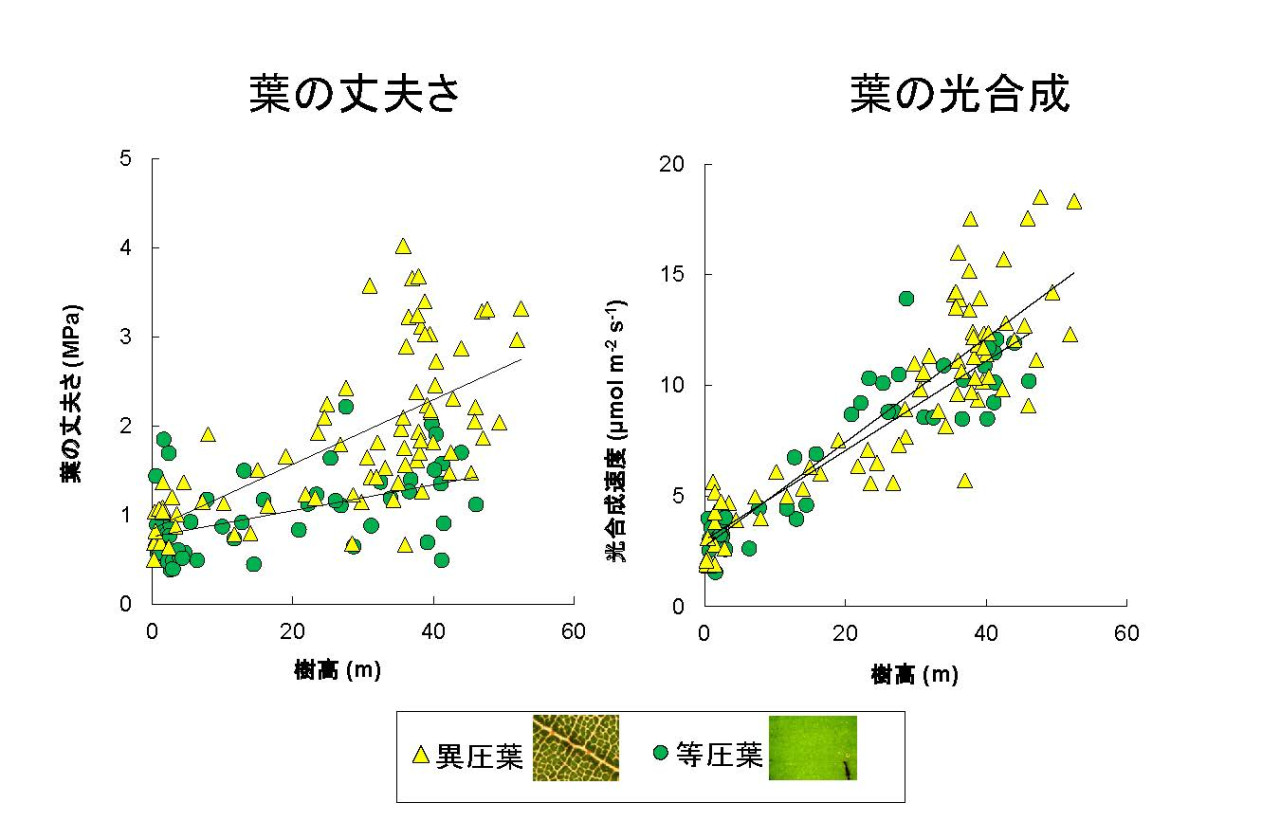
JIRCAS has been evaluating the adaptive capacity of tropical forest trees to the environment and developing afforestation technology to enhance forestry productivity and environmental adaptability through the combination of tree species suitable for the plantation environment. In collaboration with Kochi University and the Sarawak Forest Department of Malaysia, JIRCAS has now revealed that the leaf vein structure of trees in Malaysian tropical rainforest is closely related to leaf toughness and photosynthetic capacity
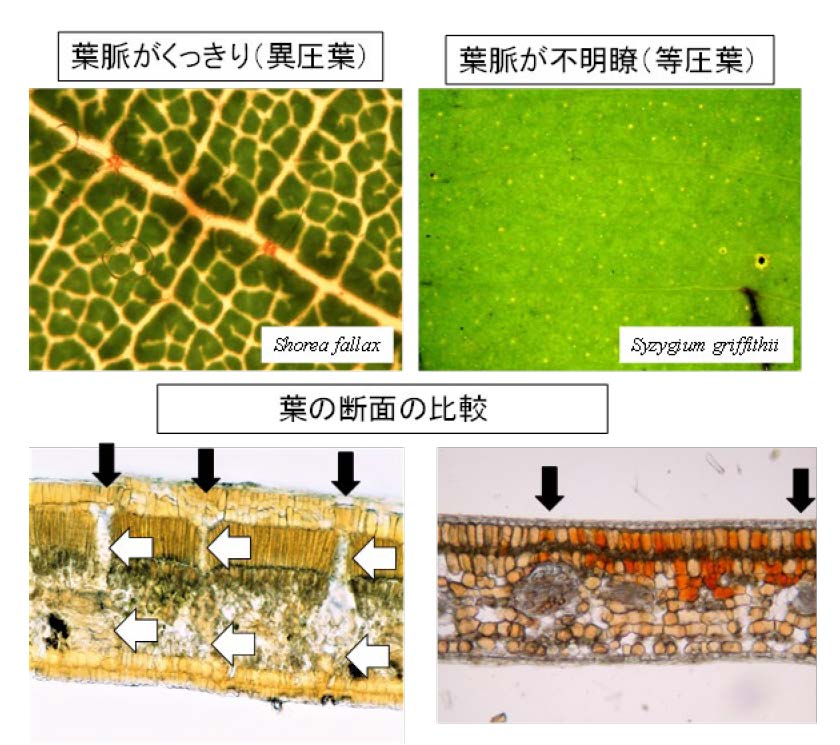
Plant eaters such as insects and herbivores, and light intensity increase from the ground toward the forest canopy. Therefore, trees need to have sturdier leaves as they grow taller, and higher photosynthetic capacity is more advantageous. Leaves are classified by species into two types: leaves with transparent fibrous tissue (bundle sheath extensions) around the vascular bundles that clearly show the veins when the leaf is exposed to light (heterobaric leaves), and leaves without this tissue, in which the veins are difficult to see (homobaric leaves). Heterobaric leaves have fibrous tissue, which makes them sturdier, but also allows more light to penetrate into the leaf and increase the photosynthetic capacity of the leaf as a whole. In other words, trees with heterobaric leaves have both high photosynthesis and leaf defense, which is advantageous in bright, high-coverage environments such as forest canopies. On the other hand, homobaric leaves, with their gapless arrangement of chloroplast-bearing cells instead of fibrous tissue, are able to utilize weak light more efficiently, which is advantageous in darker environments near the forest ground surface.
In order to enhance environmental adaptability in afforestation, it is important to select tree species that are suitable for the environment of the plantation site. Understanding of the leaf vein structure is expected to enable the selection of tree species suitable for the environment among diverse tropical rainforest tree species and the implementation of afforestation that considers the functional characteristics of the tree species.
The results of this research were published in the scientific journal Frontiers in Forests and Global Change on November 9, 2022 (JST)
Publication
- Authors
- Tanaka Kenzo, Mohizah Mohamad, Tomoaki Ichie
- Title
- Leaf toughness increases with tree height and is associated with internal leaf structure and photosynthetic traits in a tropical rain forest
- Journal
- Frontiers in Forests and Global Change
DOI : https://doi.org/10.3389/ffgc.2022.1002472
For Inquiries
JIRCAS President KOYAMA Osamu
- Program Director
- HAYASHI Keiichi (Environment Program)
- Principal Investigator
- TANAKA Kenzo (Forestry Division)
- Press Coordinator
- OMORI Keisuke (Head, Information and Public Relations Office)
E-mail:koho-jircas@ml.affrc.go.jp