Solubility improvement of African low-grade phosphate rock through calcination with potassium carbonate
Description
Although many phosphate deposits have been found in sub-Saharan Africa, farmers are facing high prices of P fertilizers because of the low solubility of the African low-grade phosphate rocks (PRs). We have previously reported that PR calcination with Na carbonate improves the solubility of these PRs, but their application showed limited crop growth, especially in upland conditions. It was speculated that Na accumulation in the soil caused plant growth inhibition. Therefore, we tried to elucidate the effect of calcination with potassium carbonate (K2CO3) on PR solubility and its application effects for lowland rice and maize through pot experiments.
We used Kodjari PR produced in Burkina Faso for the calcination. Fine powdered PRs were mixed with K2CO3 in five doses to achieve the target K2O compositions of 200, 250, 300, 350, and 400 g kg-1. The mixtures were pressed with distilled water to form coin-shaped pellets. Then, the pelletized PR-K2CO3 mixtures were calcined at 900, 1000, 1050, and 1100 °C for 10 min using a muffle furnace. The pot experiments were conducted for 56 days, monitoring the growth of rice and maize under several application rates.
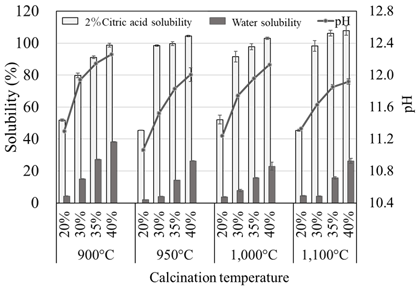
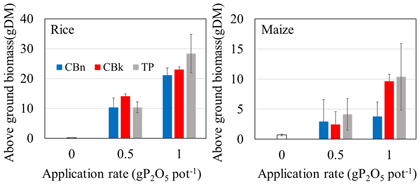
As a result, the solubility reached about 100% in 20 g L-1 citric acid and about 40% in water. This shows that K carbonates behave like Na carbonate in the solubilization of low-grade PRs in Burkina Faso. The calcinated Burkina PR (CB) application in the application rates up to 1 g P2O5 pot-1 yielded comparable plant growth to that of triple super phosphate (TP). K carbonate calcination deterred Na accumulation in the soil, and it was effective for soil P fertility improvement and plant growth. The calcination technology can be conducted by external heating U-turn rotary kiln using solar power.
Figure, table
-
Fig. 1. Solubility changes of Burkina Faso phosphate rock through calcination with several compounding rates of potassium carbonate under four levels of temperature
Error bars are standard errors (n =3) -
Fig. 2. Application effects of phosphate rocks calcinated with Na carbonate and K carbonate on rice and maize
Error bars are 95% confidence intervals (n=3). CBn: Calcinated PR with Na carbonate, CBk: Calcinated PR with K carbonate, TP: Triple super phosphate -
Table 1. Soil chemical properties after several phosphate fertilizer applications
None: No P application, BP: Burkina Faso PR, CBk: Calcinated PR with K carbonate, TP: Triple super phosphate. Bray I, and Bray II are available P content determined by Bray I method and Bray II method, respectively. Alphabet difference indicates significant differences (p<0.05) by Tukey HSD method.Crop/
Soil water conditionFertilizer pH EC Available P Exchangeable cation Bray I Bray II Ca Mg K Na mS m-1 mgP kg-1 cmolc kg-1 Rice/ None 5.84 c 108 c 0.08 b 6.39 d 3.31 c 0.70 bc 0.28 b 0.15 c Submerged BP 5.72 c 110 c 0.16 b 107 c 3.18 c 0.64 c 0.24 b 0.16 c CBk 6.45 a 183 a 6.34 a 141 a 10.20 a 0.78 b 6.67 a 0.28 a TP 6.10 b 141 b 4.94 a 117 b 5.42 b 1.09 a 0.47 b 0.24 b Maize/ None 5.85 a 114 b 0.09 b 6.77 c 3.39 c 0.69 b 0.30 b 0.14 c Upland BP 5.70 a 123 b 0.17 b 96.1 b 3.56 c 0.69 b 0.33 b 0.15 c CBk 5.97 a 189 a 5.81 a 158 a 9.36 a 0.73 b 6.39 a 0.21 b TP 6.28 a 168 a 5.69 a 107 b 5.90 b 1.11 a 0.49 b 0.24 a -
Fig. 3. External heating U-turn rotary kiln for calcination (Burkina Faso, INERA-Kamboinse)
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Crop, Livestock and Environment Division
- Classification
-
Technical A
- Program name
- Term of research
-
FY2019 (FY2016-FY2021)
- Responsible researcher
-
Nakamura Satoshi ( Crop, Livestock and Environment Division )
ORCID ID0000-0002-0952-5618KAKEN Researcher No.: 00749921Nagumo Fujio ( Crop, Livestock and Environment Division )
KAKEN Researcher No.: 20399372Kanda Takashi ( Institute for Agro-Environmental Sciences, NARO )
Imai Toshio ( Taiheiyo Cement Corporation )
Sawadogo Jacques ( Environmental Institute for Agricultural Research, Burkina Faso )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2019.1598236
Nakamura S et al. (2019) Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 65(3):267-273
- Japanese PDF
-
2019_A06_A4_ja.pdf944.38 KB
2019_A06_A3_ja.pdf221.97 KB
- English PDF
-
2019_A06_A4_en.pdf289.77 KB
2019_A06_A3_en.pdf283.94 KB
- Poster PDF
-
2019_A06_poster_fin.pdf424.82 KB