Yam Variety Identification Toolkit: Sample bulking
Sample bulking method– why it is needed?
As a part of “Yam Variety Identification Toolkit”, we propose “Sample bulking method” which has high potential to reduce time and cost, especially in quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) of large-scale propagation of yam seed tuber.
Use of “Minimum set of SSR markers” can reduce the cost of variety identification process by simply minimizing the number of PCR and gel electrophoresis conducts as described in Step 1. This proposed “Sample bulking method” could reduce the cost and time per plant drastically.
Based on high detection power of SSR marker system
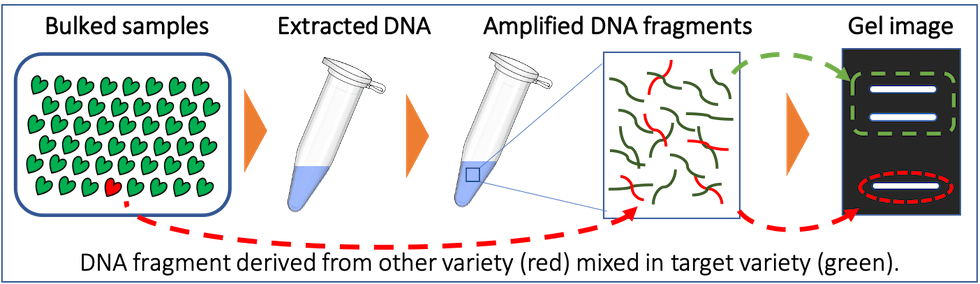
This proposed “Sample bulking method” is just utilizing high detection power of SSR marker system. By single DNA extraction from bulked leaf samples from the plants and PCR process, the band pattern based on the expected band sizes could indicate whether any mixture from other varieties or not.
With our extensive trial, we confirmed that single plant from another variety in other 100 plants from same variety can be detected comfortably through DNA extraction and PCR of the bulked tissue sample*.
*Note: Currently we only confirm this “Sample bulking method” with leaf samples. Further confirmation on the availability of tuber skin samples for “Sample bulking method” will be done.
Suit to large-scale seed propagation system to control the quality of products
This “Sample bulking methods” would suits to large-scale seed propagation, which requires high quality seed and genetically uniform to sell in yam seed market. This method provides tool to confirm the seed tuber produced is genetically pure at low cost, if you can specify the yam material grown in the premises which potentially mixed each other during the propagation process.
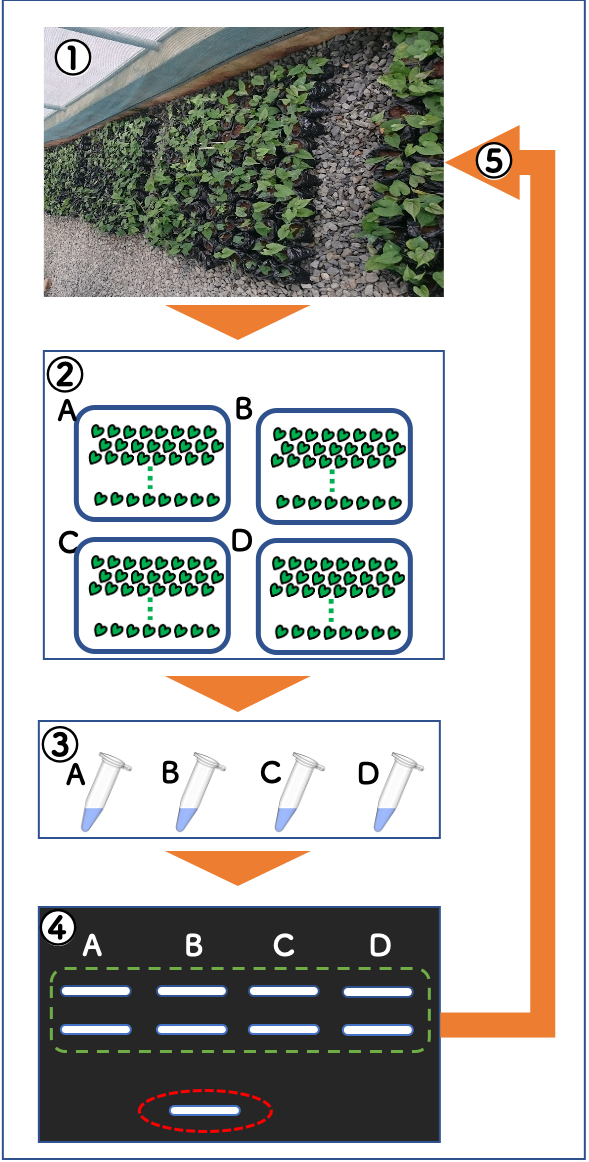
Example of use case in the large-scale seed propagation system is;
1) Manage plants of target variety in batch system (approx. 100 plants).
2) Take young leaf sample of all individual plants in each batch and bulk them.
3) Extract DNA from bulked sample and conduct PCR with suitable SSR marker(s).
4) Conduct gel electrophoresis to observe the band pattern and confirm whether any unexpected band pattern found or not.
e.g. Batch B might include the plant(s) of another variety (red circle) mechanically mixed to the plants of target variety (green square).
5) Remove mixed plants.
e.g. Eliminate all plants in batch B which potentially include the plant from other variety.
How to apply to actual works
Above is just an example. We believe proposed “Sample bulking method” could be applied to various works. And with the combination of “minimum set of SSR marker” will drastically reduce the cost of work per plant.
If you have any new case example, please communicate with us through our inquiry form. It will help other users.