Processing of high-quality rice noodles in China
Description
[Objectives]
Rice noodles are a traditional food, widely consumed in southern China and Southeast Asia. Various types of rice noodles have been produced during the long history of food processing; in China, most manufacturing has traditionally been carried out by small shops or producers (Photo 1). To industrialize the rice noodle industry, it is necessary to gather basic knowledge about the production process. Towards this objective, a study on the effects of rice varieties, soaking time and milling methods was conducted by the Food Science and Technology Division, JIRCAS.
[Results]
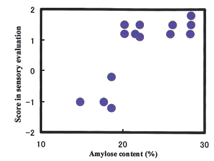
Generally, Indica rice varieties are used in rice noodle processing. Rice noodle structure depends on the gelatinization and retrogradation properties of starch, and noodle quality is believed to be highly dependent upon amylase content. To determine the influence of rice varieties, the correlation between amylase content and rice noodle quality was analyzed for two Japonica varieties, five Indica varieties and three hybrid Indica varieties. The rice noodles made from the high amylose (greater than 20%) Indica varieties achieved high scores in sensory evaluation (Fig. 1).
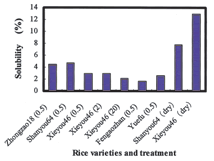
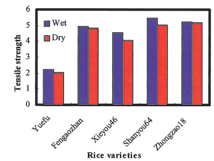
Grinding of rice granules is the first step in rice noodle processing, affecting rice flour in terms of particle size distribution, degree of gelatinization and damaged starch content. The effects of dry and wet milling of rice granules were determined, with results showing that the damaged starch content of rice flour after dry milling was greater than that after wet milling. Other results showed that 1) rice granules reached plateaus in water absorbency after soaking for two hours, 2) cooking loss of rice noodles was remarkably decreased through soaking treatment (Fig. 2), and 3) rice noodles made from wet milled flour had higher values in gel strength (Fig. 3).
Figure, table
-
Photo 1. Rice noodle processing in China. -
Fig. 1. Correlation between amylose content of rice materials and rice noodle quality. -
Fig. 2. Cooking loss of rice noodles under different soaking times (hr). -
Fig. 3. Effects of milling methods on rice noodle gel strength.
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Food Science and Technology Division
-
China Agricultral University
- Term of research
-
FY2001 (FY1997-2003)
- Responsible researcher
-
TATSUMI Eizo ( Food Science and Technology Division )
CHENG Minghua ( China Agricultral University )
LI Lite ( China Agricultral University )
LI Zaigui ( China Agriculture University Japan-China Food Research Center )
JIANG Zhengqiang ( China Agricultral University )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
M. Cheng, L. Li and E. Tatsumi (2000):Influences of Rice Varieties and Grinding Processes on Rice Flour Characteristics. Cereal & Feed Industry (in Chinese), 8, 16-19.
M. Cheng, L. Li and E. Tatsumi (2000):The Evaluation Systems of Non-fermented Rice Noodle. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association (in Chinese), 15(5), 14-18.
- Japanese PDF
-
2001_17_A3_ja.pdf721.68 KB
- English PDF
-
2001_14_A3_en.pdf708.41 KB