The function of tomato mitochondrial small heat shock protein under heat stress conditions
Description
[Objectives]
Heat stress is one of the most significant constraints on crop production. Under heat stress, synthesis of most proteins is repressed and some proteins, which are called heat shock proteins (HSPs), begin to be synthesized. Accumulation of sHSP in mitochondria (MT-sHSP) under heat stress has recently been reported in a number of plant species, but little is known about the cellular functions of MT-sHSP in the heat tolerance of plants.
The aim of this study was to clone MT-sHSP cDNA from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) leaves, evaluate the transcription of the MT-sHSP gene at various temperatures, and assay the molecular chaperone activity of MT-sHSP in vitro.
[Results]
A full-length cDNA (LeHSP23.8: accession number AB017134) encoding the precursor of the MT-sHSP in tomato was successfully cloned. The deduced protein precursor, had a calculated molecular weight of 23.8 kDa.
A single copy of LeHSP23.8 was found in tomato genomic DNA through Southern-blot analysis.
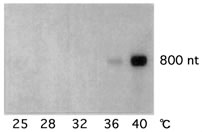
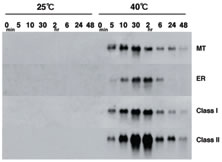
Northern blot analysis revealed the heat-inducible character of LeHSP23.8 mRNA. The threshold temperature was approximately 36℃, and it was accumulated abundantly at 40℃ in tomato leaves (Fig. 1). Among the MT-, ER-, Class I and Class II-sHSP genes, MT-sHSP mRNA responded most quickly at 40℃ in tomato flowers (Fig. 2).
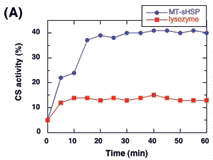
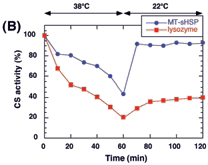
The molecular chaperone function of LeHSP23.8 was demonstrated in vitro. When the recombinant LeHSP23.8 was mixed with CS denatured by guanidine hydrochloride, 40% of the native CS activity was recovered after one hour of incubation (Fig. 3A). In another experiment, recombinant LeHSP23.8 protected CS from thermal inactivation and also promoted the renaturation of thermally inactivated CS. The loss of CS activity was relatively slow when CS was incubated with recombinant LeHSP23.8 at 38℃. Furthermore, when the incubation temperature was shifted to 22℃, rapid renaturation of thermal-denatured CS was observed within 10 minutes, and 90% of CS activity was recovered (Fig. 3B).
Figure, table
-
Fig. 1. Northern-blot analysis of temperature-dependent LeHSP23.8 mRNA accumulation in tomato leaves. Tomato plants were grown in greenhouse conditions at 25℃ and treated at 28℃, 32℃, 36℃ or 40℃ for two hours. -
Fig. 2. Northern-blot analysis of heat-induction time course for sHSP genes in tomato flowers. Tomato plants grown under greenhouse conditions were transferred to the growth chamber on the day of flowering, and then incubated at 25℃ or 40℃. The flowers were collected 0 min to 48 hours after the incubation. Panels MT, ER, Class I and Class II show the expression of the genes for MT-, ER-, Class I- and Class II-sHSP, respectively. -
Fig. 3. (A) Effects of LeHSP23.8 protein on the renaturation of chemically denatured citrate synthase (CS). CS (15μM) was denatured in 6 M guanidine hydrochloride for 120 minutes and then diluted 100-fold into a solution supplemented with 150 nM lysozyme ( ) or with 1.8 μm recombinant LeHSP23.8 (
) or with 1.8 μm recombinant LeHSP23.8 (  ). (B) Effects of recombinant LeHSP23.8 on the thermal inactivation of CS. CS (150 nM) was incubated in the presence of 150 nM lysozyme (
). (B) Effects of recombinant LeHSP23.8 on the thermal inactivation of CS. CS (150 nM) was incubated in the presence of 150 nM lysozyme (  ) or 1.8 μm recombinant LeHSP23.8 (
) or 1.8 μm recombinant LeHSP23.8 (  ) at 38℃ for 60 minutes and then at 22℃.
) at 38℃ for 60 minutes and then at 22℃.
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Okinawa Subtropical Station
-
Shandong Teacher University, China
Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research, India
Land Resources Research Institute, Pakistan
Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution
- Classification
-
Technical A
- Term of research
-
FY2001 (FY1998-2005)
- Responsible researcher
-
SHONO Mariko ( Okinawa Subtropical Station )
LIU Jian ( Shandong Teacher University, China )
SINGH Ishwar ( Indian Institute of Sugarcane Research, India )
DIN Jaral Ud ( Land Resources Research Institute, Pakistan )
SANMIYA Kazutsuka ( Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution )
SUZUKI Katsumi ( Okinawa Subtropical Station )
TSUKAGUCHI Tadashi ( Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution )
EGAWA Yoshinobu ( Okinawa Subtropical Station )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
J. Liu and M. Shono (1999): Characterization of mitochondria-located small heat shock protein from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Plant and Cell Physiology, 40, 1297-1304.
- Japanese PDF
-
2001_22_A3_ja.pdf850.9 KB
- English PDF
-
2001_19_A4_en.pdf115.29 KB