Mitigation of nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soil by 2-amino-4-chloro-6-methylpyrimidine
Description
Agricultural soil is the largest anthropogenic source of nitrous oxide (N2O), a greenhouse gas. Nitrification inhibitors have been used to increase fertilizer efficiency and to mitigate nitrogen leaching. They also decrease N2O emissions from agricultural land. 2-chloro-6 (trichloromethyl) pyridine (nitrapyrin) is a strong nitrification inhibitor that has been used with liquid ammonia in the USA. However, it cannot be amended to solid fertilizer because of its low solubility and high volatility. To select an alternative nitrification inhibitor that is easy to handle and which will effectively mitigate N2O emissions from the soil, 2-amino-4-chloro-6-methylpyrimidine (AM), sulfathiazole and 1-aryl-2-thiourea were compared. These chemicals can be amended into solid fertilizer.
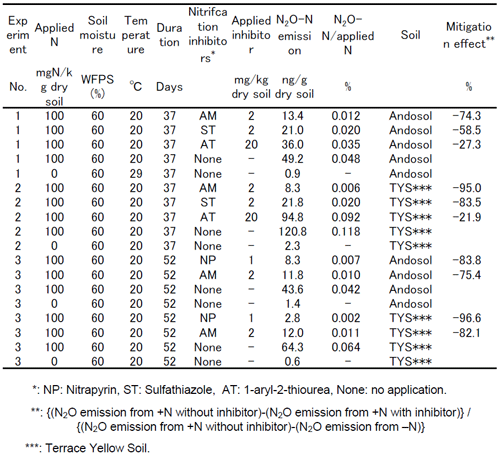
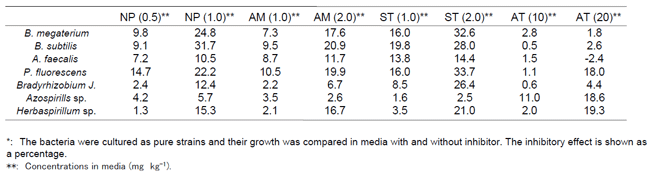
The results of soil incubation experiments showed that AM mitigated N2O emission from soil where nitrogen fertilizer had been applied. The effect of AM on reducing N2O emissions was weaker than nitrapyrin but stronger than sulfathiazole and 1-aryl-2-thiourea (Table 1). Application of AM did not inhibit soil respiration. The side effects of AM on 7 bacterial species that contribute to agricultural production in the field were tested. AM proved to inhibit the growth of these bacteria to the same degree as other inhibitors (Table 2). These results show that AM selectively inhibits nitrification bacteria and that the side effects on other bacteria are minor. It was concluded that AM can be used to mitigate N2O emissions from agricultural soil as an alternative to nitrapyrin.
Figure, table
-
Table 1. Effect of nitrification inhibitors on mitigating N2O emissions (Soil incubation experiment).
-
Table 2. Inhibitory effects of nitrification inhibitors on 7 bacteria useful in agriculture.
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Crop Production and Environment Division
- Classification
-
Technical A
- Term of research
-
FY2005(FY2003~2005)
- Responsible researcher
-
WATANABE Takeshi ( Crop Production and Environment Division )
TRIMURTULU Nunna ( Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
Takeshi Watanabe (2006): Influence of 2-chloro-6 (trichloromethy) pyridine and dicyandiamide on nitrous oxide emission under different soil conditions, Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 52(2), 226-232
Takeshi Watanabe (2004): Abstracts of the annual meeting, Japanese Society of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 192
- Japanese PDF
-
2005_seikajouhou_A4_ja_Part7.pdf477.6 KB