Local name
Mam-khai-plaa
Som-khai-plaa
Som-khai-plaa-jeen
Khai-plaa-dorng |
Ingredients
Fish eggs and flesh.
In some provinces the air bladder is also used.
Salt, cooked glutinous rice. |
Fish normally used:
Cyprinus carpio (Nai)
Ctenopharyngodon idellus (Chao-hue)
Hypopthalmichthys molitrix (Leng-hue, Jeen)
Puntius gonionotus (Ta-pian)
Pangasius hypophthalmus (Sa-waai) |
| Fermentation: |
2-3 days. |
| Storage life: |
7 days. |
| Production: |
In home industry in the North and Northeast. |
| Properties: |
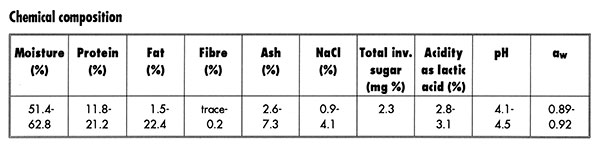
Semi-solid, sticky of pink or orange colour with sour and salty taste. The portion at the surface in the container which contacts with the air turns black. The fat content varies, largely depending on species of fish used. |
Microorganisms
Lactobacillus sp.
|