Development of individual based-model for simulating the spread of Citrus greening disease by the vector insects
Description
Citrus greening disease (Huanglongbing, HLB) is an untreatable disease that makes trees wither and die. Therefore, in order to prevent HLB spread in citrus orchards, especially in the severely affected areas such as Southern Vietnam, a vector insect management strategy based on infection risk is required. To estimate the HLB infection risk by the vector in an orchard, we developed a simulation model following a framework of individual-based model (IBM).
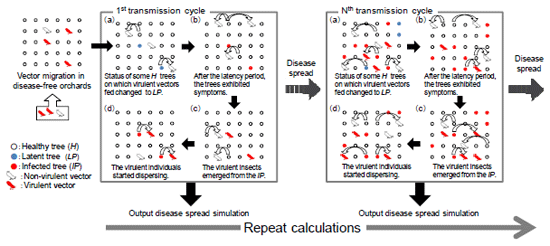
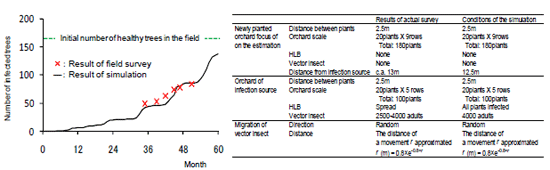
As a basis for developing IBM, the C language technology of simulated individuals was electronically published on “http://gi.ics.narawu.ac.jp/~takasu/research/IBM/ibm.html”. IBM differs from existing models such as the lattice model. Our IBM is able to provide parameters for each individual citrus tree and the vector (Table 1). Therefore, it is able to examine the disease spread dynamics in the simulation field, by calculating the cumulative results of the individual behaviors. In our model, the process was divided into the following four periods (Fig. 1) (a. Some of the citrus trees which were fed on by the virulent vector insects changed their status to the latency or incubation period. b. After the latent period, the trees exhibited the symptoms of HLB. c. The virulent insects emerged from the infected trees. d. Then, the virulent individuals started dispersing.). The result of the simulation in the newly planted citrus orchards in southern Vietnam near the infected field showed a similar trend with the actual survey (Fig. 2). In our model, by changing the parameters of each individual vector insect and the host trees, it was possible to quickly and reasonably examine the synergistic effect of the combination of each of the control techniques.
A validation test is necessary before an extension of the simulation results can be performed. It is possible to develop new management techniques by estimating the effective parameters to prevent the spread of HLB. By changing the parameters of this model, we can simulate the spread dynamics of other diseases which are likewise infected through vector insects.
Figure, table
-
Table 1 Parameters of developed model.
-
Fig. 1 Summary of Citrus greening disease spread simulation by the individual based model.
The model is able to provide parameters for each individual citrus tree and the vectors. -
Fig. 2 Comparison between the results of the simulation and results of the actual survey.
The simulation conditions are referred to in the table to the right.
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Tropical Agriculture Research Front
- Classification
-
Administration B
- Term of research
-
FY2006~2010
- Responsible researcher
-
Kobori Youichi ( Crop, Livestock and Environment Division )
OHTO Yasuo ( Tropical Agriculture Research Front )
NAKATA Tadafumi ( Tropical Agriculture Research Front )
TAKASU Fugo ( Nara Women’s University )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
Kobori et al. (2011) JIRCAS Working Report No.72
Kobori et al. (2011) Appl. Entomol. Zool. 46:27–30.
- Japanese PDF
-
2010_seikajouhou_A4_ja_Part30.pdf111.19 KB