Interlinkage in the rice market of Ghana: Money-lending millers enhance efficiency
Description
[Objectives]
The development of local agricultural markets plays a crucial role in the agricultural development of developing countries. Due to recent trade liberalization, the importance of local agricultural markets has further increased. One of the significant aspects of rural economies is interlinked transaction. By studying the nature of interlinkages in a particular region, we will be able to identify the constraints of market development and implement new policies to facilitate further development. Following along these lines, this study has analyzed rice markets in Ghana, particularly focusing on rice millers. Millers are key players in Ghana’s rice market. The millers mill the paddy and charge producers for milling fees. After milling, the producers sell milled rice to traders through those millers. Not only do they serve as middlemen, but some also provide rice producers with funds on a loan basis under the agreement that they will bring paddy only to that miller; surprisingly, the millers do not charge interest in most cases. In order to investigate whether this interlinkage between producers and millers, known as “Pareto,” is improving and evolving, a study was conducted to examine the effects of the millers’ no-interest loans on the efficiency of their milling operations.
To this end, we estimated a short-run quadratic cost function for the millers and evaluated the impact of money-lending on the operating rate. As experimental subjects, 61 millers were randomly selected from the Kumasi area in Ghana. We interviewed miller owners and their operators to obtain information on each mill and their milling activities in 2001. For this study, we used “capacity utilization” as the operating rate index and a two-stage regression method to control “self-selection bias.”
[Results]
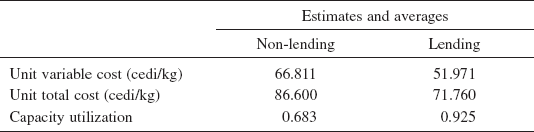
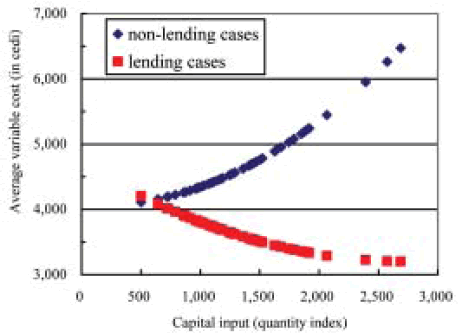
Table 1 shows the estimated costs and capacity utilization of money-lending and non-lending cases, and Fig. 1 indicates the relationship between capital input and average variable cost for each case. The results suggest that the operation rate of the mills increases by 24% if farmers are provided with loans. In addition, the total cost should decrease by 17.1% when compared to situations in which farmers are not provided with loans, and thus increase efficiency. Based on this interlinkage transaction, we can conclude as the following: (1) the amount of paddy collection increases by providing farmers with loans; (2) the operation rate and efficiency of millers increase; and (3) the farmers are able to obtain credit with little or no interest.
Nevertheless, the emergence of this interlinkage underlines the inefficiency of the Ghanaian rice market. Although our data suggests that relatively larger mills are more technically efficient, the millers cannot fully optimize their utilization capacity due to the underdevelopment of transportation and paddy storage, as well as the difficulty of obtaining market information. Large-scale mills should be promoted in Ghana, not only because of their superior efficiency, but also because of their better milling potential, both of which will enhance the competitiveness of local rice production. Efficiency of the rice markets may not improve as expected without complementary policies to develop efficient transportation, storage facilities to alleviate seasonal fluctuations of operation efficiency rates, and information systems to relay current demands for paddy milling.
Figure, table
-
Table 1. Costs and capacity utilization.
-
Fig. 1. Simulation results of capital input and average variable costs. (8,600 cedi = 1 US$).
- Affiliation
-
Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences Development Research Division
- Classification
-
Technical A
- Term of research
-
FY2002 (FY2001, FY2000)
- Responsible researcher
-
FURUYA Jun ( Development Research Division )
- ほか
- Publication, etc.
-
Furuya, J. and Sakurai, T. (2003): “Interlinkage in the Rice Market of Ghana : Money-lending Millers Enhance Efficiency”. Contributed paper selected for presentation at the 25th International Conference of Agricultural Economists,
http://www.iaae-agecon.org/conf/durban_papers/papers/088.pdf.Furuya, J. and Sakurai, T. (2002): “Efficiency Gains by Money Lending: The Case of Rice Millers in Ghana”. Program and abstract of 9th JIRCAS International Symposium, 25.
Furuya, J. (2003) ARDEC (28), 11-16.
- Japanese PDF
-
2003_02_A3_ja.pdf1.18 MB
- English PDF
-
2003_02_A4_en.pdf48.23 KB